11401. Game
In their free time, Fidan and Fuad like to
play games at home. This time, they came up with a new game:
·
Fuad
takes a blank sheet of paper.
·
Fidan
says a number. If this number is already written on the paper, Fuad erases it.
Otherwise, if the number is not on the paper, he writes it down. This process
is repeated n times.
·
At the
end of the game, Fidan needs to determine how many numbers remain written on
the paper.
The numbers said by Fidan are given as a
sequence a1, a2, ..., an
– in the exact order she says them. Help Fidan determine how many distinct
numbers remain on the paper at the end of the game.
Input. The first line contains a single integer n (1
≤ n ≤ 105). The second line contains n integers
a1, a2, ..., an
(1 ≤ ai ≤ 109).
Output. Print the count of numbers that remain on the paper at
the end of the game.
|
Sample
input 1 |
Sample
output 1 |
|
4 5 7 4 5 |
2 |
|
|
|
|
Sample
input 2 |
Sample
output 2 |
|
6 1 2 3 2 3 1 |
0 |
SOLUTION
data structures – set
Algorithm analysis
We will
simulate the game using a data structure – a set. The set will store all the
numbers currently written on the paper.
Each time
Fidan says a number, Fuad checks whether it is in the set:
·
if it is – he removes the number from the set
(erases it from the paper);
·
if it is not – he
adds the number to the set (writes it on the paper).
The number
of elements remaining on the paper at the end of the game is equal to the
number of elements in the set.
Example
Let’s
simulate how the set behaves for the first and second examples.
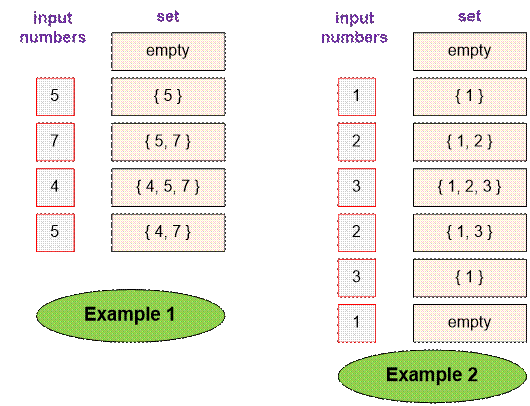
At the end
of the game:
·
The first set contains 2 elements;
·
The second set is empty (contains 0 elements).
Algorithm implementation
Read
the number of elements n.
scanf("%d", &n);
Process
the n numbers said by Fidan one by one.
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
scanf("%d", &x);
Each
time Fidan says a number x:
·
If the number x is not in the set, we add it.
·
If the number x is already in the set, we remove it.
if
(s.find(x) == s.end())
s.insert(x);
else
s.erase(x);
}
Print
the answer – the size of the set s.
printf("%d\n", s.size());
Python implementation
Read
the input data.
n = int(input())
lst = map(int,input().split())
Declare
a set.
s = set()
Process
the numbers said by Fidan one by one.
for x in lst:
Each
time Fidan says a number x:
·
If the number x is already in the set, we remove it.
·
If the number x is not in the set, we add it.
if x in s:
s.remove(x)
else:
s.add(x)
Print
the answer – the size of the set s.
print(len(s))